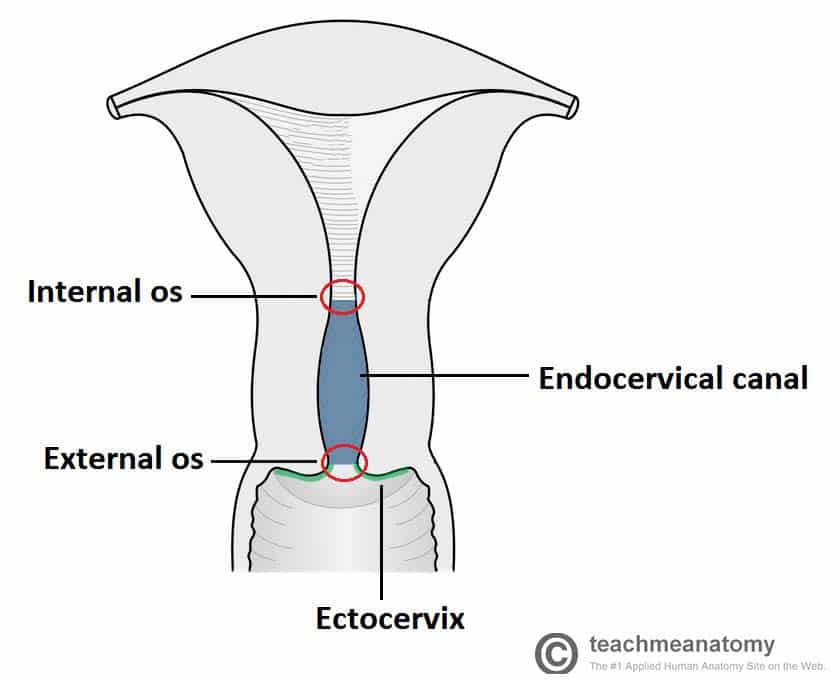
Describe the Locations of the Internal and External Cervical Os
Isthmus - the constricted part of the uterus located between the body and the cervix. Running through the cervix is an opening called the os with the end that opens into the vagina called the external os and the.

Internal Os Anatomy Britannica
Also located in the cervical spine region are the carotid arteries.

. The cervical opening into the vagina is called the external os. Its lower half or intravaginal part lies at the upper end of the vagina and its upper half lies above the vagina in the. An opening in the center of the ectocervix known as the external os opens to allow passage between the uterus and vagina.
In human reproductive system. It is lined by stratified squamous non-keratinized epithelium. There are three parts of the cervix.
THE 2 COMMUNICATE VIA AN ISTHMUS one on inside one on. External opening of the canal into the vagina Vagina The vagina is the female genital canal. The endocervix or endocervical canal is a tunnel through the.
Describe the locations of the internal and external cervical os. The endocervix endocervical canal is a luminal cavity within the cervix forming a passageway between the external os and the internal os. The opening on the outermost vaginal side of the canal.
Main tributaries of the vertebral arteries the cervical radicular arteries supply blood directly to the cervical vertebral bodies. Internal opening of the canal into the uterine body. The cervix occupies both an internal and an external position.
The opening in the ectocervix the external os marks the transition from the ectocervix to the endocervical canal. The external os is where the cervix opens into the vagina. Cervix - the inferior.
It makes up a large portion of the basilar part of the neurocranium and entirely. The occipital bone is an unpaired bone which covers the back of the head occiput. The internal os is the aperture of the junction between the corpus uteri and the cervix the external os is where the cervix opens into.
Describe the locations of the internal and external cervical os CERVICAL OS IS THE DIRECT OPENING TO THE CERVIX. The cervix only about 4 centimetres 16 inches long projects about 2 centimetres into the upper vaginal cavity. Internal os is the aperture of the junction between the corpus uteri and the cervix.
Mucus-producing cells that form the upper two-thirds of the cervix. Uterine structurethe vagina is called the external os of the uterus. It has a narrow central canal which runs along its entire length connecting the uterine cavity and.
The internal os is part of the cervix which forms the neck of the uterus part of the female reproductive system. The cervix is usually 2 to 3 cm long and roughly cylindrical in shape which changes during. Rarely you will encounter a situation where the cervix seems to be dilated to 6 cm but on further investigation you find a 2cm opening posterior to what you first felt.
The center of the. Women the external os resembles a small circular opening in the centre of the cervix. The upper limit of the endocervical canal called.
The supravaginal portion meets with the muscular body of the uterus at the internal cervical os. List the three layers of the uterine wall. The body has a base fundus and an internal chamber uterine cavity.
The cervical canal communicates with the uterine cavity via the internal orifice of the uterus or internal os and with the vagina via the external orifice of the uterus ostium of. The lowest part which can be seen from inside the vagina during a gynecological exam is called the ectocervix. The external os is small almost circular and often depressed.
The cervix or cervix uteri is the lower part of the uterus in the human female reproductive system. Its proximal portion is located in the abdomen and its distal portion in the vagina.

Internal Os Anatomy Britannica

Cervix Definition Function Location Diagram Facts Britannica

A Cross Sectional View Of The Cervix The Uterus Is Above The Internal Download Scientific Diagram
The Cervix Structure Function Vascular Supply Teachmeanatomy
No comments for "Describe the Locations of the Internal and External Cervical Os"
Post a Comment